A complete guide to customer engagement strategy for 2026
Published on January 28, 2026/Last edited on January 28, 2026/19 min read


Madison Tiemtoré
Content Marketing Lead, BrazeContents
- What is a customer engagement strategy (and why it matters now)?
- Digital customer engagement strategy vs. CRM and traditional marketing
- The core pillars of a modern customer engagement strategy
- How to create a customer engagement strategy (step by step)
- From tactics to journeys: Core customer engagement strategies every program needs
- Which channels power an effective customer engagement strategy?
- Data, privacy, and trust in customer engagement strategy
- How AI and automation improve customer engagement strategy
- Customer engagement strategy examples from leading brands
- How to measure customer engagement strategy success
- Common customer engagement strategy mistakes (and how to avoid them)
- Customer engagement strategy FAQs
Customers rarely move in a straight line. They bounce between email, apps, websites, physical stores, and customer support—and they expect brands to remember what happened. A customer engagement strategy turns that messy reality into an organized system that teams can run, improve, and scale.
This guide shows how to build B2B and B2C customer engagement strategies that hold up in 2026. You’ll get practical frameworks for turning first-party data into coordinated, cross-channel journeys, plus AI-powered tactics for improving personalization, prioritization, and optimization over time.
Here's a quick overview of what we'll be discussing:
- How to navigate the complexities of modern customer journeys and create coordinated, cross-channel experiences that enhance retention, loyalty, and customer lifetime value (CLV).
- The four core pillars of customer engagement: Customer understanding, journey orchestration, personalization with AI, and measurement/optimization.
- How to set measurable outcomes, map key lifecycle stages, utilize first-party data, design personalized journeys, and incorporate AI decisioning to optimize engagement efforts across various channels.
What is a customer engagement strategy (and why it matters now)?
A customer engagement strategy is an end-to-end plan for how you build, maintain, and deepen customer relationships across lifecycle stages and channels. It connects first-party data, personalization, and cross-channel engagement so each interaction reflects what a customer did, what they care about, and what they’re likely to need next.
Having an engagement strategy matters now because the conditions around growth have changed in ways that expose weak engagement.
Acquisition costs keep rising
Paid reach is harder to sustain, and performance can swing quickly. A customer engagement strategy gives teams a clearer path to retention, loyalty, and customer lifetime value (CLV) by focusing on repeat behaviors, value moments, and habit formation.
Customer journeys are fragmented
Customers move between brand touchpoints without thinking twice, expecting an omnichannel experience. But when channels are run independently, messaging repeats, arrives out of sequence, or arrives at the wrong moment. Customer journey orchestration gives teams a way to coordinate touchpoints so that context carries forward.
Privacy changes limit third-party data
Signals that used to power targeting and personalization are less available, less reliable, and riskier to use. That pushes engagement toward first-party data and transparent value exchange—preferences, behavior, and consent-based relationships that customers can control.
Expectations for relevance and consistency keep rising
Customers compare every interaction to the best experiences they’ve had, across any brand. That raises the bar for personalization, timing, and tone, and quickly makes generic batch sends feel out of place.
A strong customer engagement strategy treats engagement as a continuous relationship, shaped by what customers do over time. Campaigns still have a role, but long-term performance comes from the journeys that run every day—onboarding, education, purchase and reorder, loyalty, and proactive engagement that steps in when customers hit friction or drift toward churn.
Digital customer engagement strategy vs. CRM and traditional marketing
A customer engagement strategy defines what you do with all of your customer data. You could say it sits in the middle of your stack, turning your brand and customer experience (CX) intent into lifecycle journeys.
A customer relationship management (CRM) solution stores customer and account information, plus interaction history, and supports workflows for teams like sales, marketing, and support. It’s designed to manage records and processes, such as contact histories, tickets, and account notes.
Traditional marketing programs often run through channel-specific campaigns and calendars. That works well for launches and promotions, but brands can struggle to stay consistent when customers move between channels and behaviors change quickly across the lifecycle.
A customer engagement platform (CEP) ties everything together. It activates first-party data in real time so teams can orchestrate cross-channel engagement based on what a customer does next.
That usually includes:
- Real-time marketing orchestration across email, push, SMS, in-app, web, and other touchpoints
- Cross-channel controls like prioritization, suppression, and frequency management
- Personalization at scale through dynamic content and timing based on preferences, behaviors, and lifecycle stages
- Measurement loops through journey-level reporting and experimentation tied to engagement metrics like retention, conversion, and LTV
The core pillars of a modern customer engagement strategy
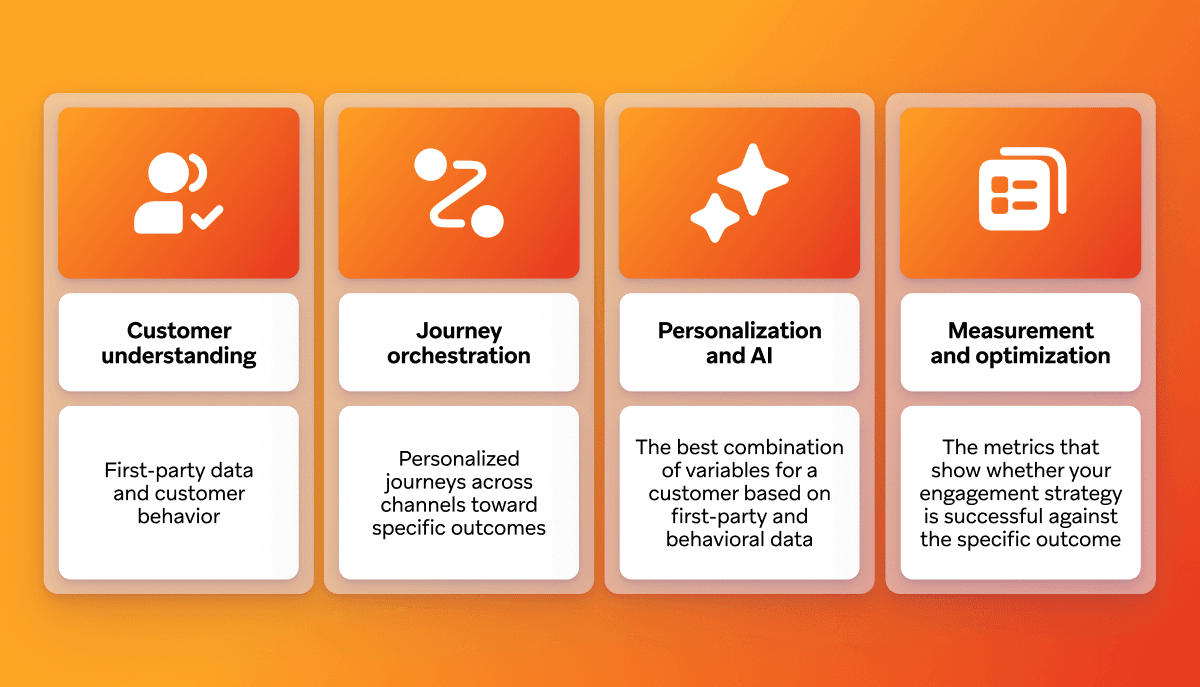
A modern customer engagement strategy has four pillars that work together to tie customer journeys (at various points in the lifecycle) back to outcomes, such as retention and loyalty.
Customer understanding
Customer understanding starts with first-party data and the signals customers generate as they browse, buy, and use your product. With clearer context, marketers rely less on guesswork.
This pillar usually includes:
- Behavioral signals tied to lifecycle marketing milestones (first purchase, second purchase, repeat category, lapsing activity)
- Preference and consent choices that shape channel selection and frequency
- Segments built around intent and value (new, active, high-value, at-risk, loyalty tiers)
Journey orchestration
Customer journey orchestration turns those signals into coordinated, personalized journeys across channels—creating more of a truly cohesive 1:1 customer experience, rather than a set of separate campaigns.
This pillar includes:
- Lifecycle journeys with clear jobs—onboarding, repeat purchase, replenishment, loyalty, win-back
- Sequencing rules so messages across email, push, SMS, in-app, and web don’t compete
- Prioritization, suppression, and frequency limits that protect the customer experience (CX)
Personalization and AI
Personalization helps build relationships with your customers, but it can sometimes be lacking or come across as creepy if it doesn’t show up in the right place, at the right time, and in the right way. A customer engagement strategy helps figure out where personalization is most useful and needed. Going a step further, AI decisioning helps select the best combinations of variables for each individual customer from a set of options you provide, based on the outcomes you care about, and it keeps learning from customer behavior over time.
The personalization and AI pillar often includes:
- Dynamic content and offers based on browsing, purchase history, loyalty status, and preferences
- Predictive audiences for churn risk, conversion likelihood, repeat purchase propensity, and upsell readiness
- Decisioning across message variables: Content modules, offers, products, channel, delivery timing, and frequency, guided by business goals and guardrails
Measurement and optimization
Measurement connects day-to-day engagement metrics to business outcomes, so teams know what to improve and where to put their time and effort.
The most useful habits are:
- Track leading indicators (engagement frequency, repeat actions, time-to-value) alongside retention and revenue
- Read performance at the journey level, not just the campaign level
- Run experiments and holdouts so you can attribute lift to specific changes
How to create a customer engagement strategy (step by step)
Creating a customer engagement strategy can feel daunting, especially when multiple teams, channels, and goals need to line up. Use these steps to help turn brand and department priorities into a cohesive plan your teams can follow, measure, and improve over time.
1. Set outcomes tied to retention, revenue, and customer value
Define success for key lifecycle stages in a way that’s measurable. Examples include reducing early churn by improving activation in the first 7 or 14 days, increasing repeat purchase rate in the first 60 days, growing upgrades by targeting high-intent users, or improving loyalty by increasing high-value customer frequency.
2. Map lifecycle stages and define the moments that matter
Turn lifecycle marketing into observable events. These moments become your triggers, journey entry points, and measurement checkpoints. Common examples include first visit or install, account creation, first key action (“aha” event), second session or repeat purchase, and inactivity thresholds that signal risk.
3. Get first-party data and consent ready for activation
This step means you’ve tracked the key actions, saved the few details that change what you send, and you know which channels you can use, so your journeys respond in a way that matches what customers actually want.
For example: A customer signs up, browses, and adds a couple of items to a wishlist, then stops.
To follow up in a way that feels relevant, you need to know:
- What they did: signed up, browsed, wishlisted items, then went quiet
- What changes the message: region, language, loyalty status, or the category they browsed
- How you can contact them: email, push, or SMS opt-in, plus any preferences they set
With that in place, you can respond based on consent and behavior:
- If they opted into push, send a short wishlist reminder the next day
- If they opted into email, send a wishlist email with the items they saved
- If they opted into SMS for price alerts, send a message only when an item drops in price
- If they opted out of everything, show an in-app message the next time they open the app
4. Build audiences around intent, value, and risk
Build audiences based on behavior and engagement frequency, such as new users who haven’t reached activation, engaged users ready for discovery or upsell, high-value customers for loyalty treatment, lapsing customers, and customers showing churn signals.
5. Design cross-channel journeys with clear entry, exit, and rules
This step is about turning a goal into a journey your team can actually run without customers getting spammed or stuck in loops. You decide who the journey is for, when it starts, what counts as success, and what happens if the customer does nothing.
Here’s a simple example: an abandoned cart.
Entry (who starts the journey): A customer adds an item to their cart but doesn’t check out within two hours.
Exit (when they stop): They purchase, they remove the item, or seven days pass.
Primary channel (where the main message lives): Email, because it’s better for product details and links back to the cart.
Supporting touchpoints (what backs it up):
- A push reminder later that day for customers who opted in
- An in-app message the next time they open the app, if they didn’t convert
Rules (so messages don’t pile up):
- Cap reminders to a small number (for example, no more than two in 48 hours)
- Don’t send if they’re already in a promotion journey, or they’ve recently received multiple messages
- Stop all reminders the moment they buy
Personalization (what makes it feel relevant):Use what they browsed or added to cart, their preferred category, and whether they respond better to email or push.
Branching (what changes based on what they do next):
- If they click but don’t buy, follow up with a product detail or reviews message
- If they don’t engage at all, pause for a few days, then try a different angle
- If they buy, move them into post-purchase and replenishment journeys instead
6. Add AI and AI decisioning where it improves choices at scale
AI can support engagement in three different ways. Predictive AI helps you understand what’s likely to happen. Generative AI helps teams create and test content faster. AI decisioning helps select the winning combinations of campaign variables for each individual customer, based on the outcome you choose to optimize for.
Practical applications include:
- Predictive AI: Identify churn risk, conversion likelihood, repeat purchase propensity, or loyalty propensity, then use those signals to prioritize journeys and outreach.
- Generative AI: Produce message variants for testing faster, including copy and creative components, within brand guardrails.
- AI decisioning: Helps select the best combination of campaign variables for each customer from the assets you provide (message variants, featured products or services, promotions, channels, and delivery timing and frequency), then keep learning from live interactions to improve future outcomes.
7. Measure early, then improve through testing
Start measuring from day one so that you know what to address first. In the first few weeks, focus on how quickly people reach value, where they stall in onboarding, and whether your messaging is driving opt-outs or unsubscribes. Test changes as you go, and track what moves retention and revenue.
From tactics to journeys: Core customer engagement strategies every program needs
Single messages are easy to launch. Journeys help you stay consistent across the customer lifecycle, because they connect touchpoints and give teams a clear plan to run and improve.
Onboarding and activation journeys
Activation journeys help customers reach value quickly, based on what they’ve done so far:
- Welcome and setup messages tailored to source or goal
- In-app guidance that points customers to the most relevant step
- Nudges triggered by stalled progress
Lifecycle education and feature discovery nudges
These journeys teach customers what’s possible, without overwhelming them:
- Feature education tied to specific behaviors
- In-app prompts triggered by context, not a timer
- Follow-ups that reinforce what customers saw in-product
Revenue and growth journeys (upsell, cross-sell, loyalty)
Personalization and AI decisioning can help decide which offers, products, and messages to show, and when. Replenishment, loyalty, and time-bound offers tend to converge during peak season customer engagement, so coordination and frequency controls carry more weight. These might include:
- Cross-sell and recommendations based on browsing and purchase history
- Replenishment and repeat purchase journeys tied to timing and category behavior
- Loyalty journeys tied to milestones, frequency, and tenure
Risk, churn, and win-back journeys
It’s better to start risk journeys early rather than wait for a long lapse in engagement. Consider:
- Lighter-touch reminders when engagement drops
- Help-first messaging when friction or support issues spike
- Win-back flows based on inactivity windows and past behavior
Which channels power an effective customer engagement strategy?
A digital customer engagement strategy works best when channels play distinct roles across the lifecycle. Braze research found that brands that embrace cross-channel engagement see a 55% increase in 90-day retention.
Email is a strong fit for longer-form content and messages customers may come back to later, like onboarding series, education, receipts, and personalized recommendations.
Push notifications
Push works for timely nudges tied to what someone is doing right now, like finishing setup, returning to a cart, or picking up a streak.
SMS and MMS
SMS fits high-visibility messages where consent and expectations are clear, like time-sensitive updates, reminders, and loyalty perks for high-value customers.
In-app messages
In-app messages help at the moment of action, when intent is highest. They’re useful for reducing friction, guiding next steps, and supporting feature discovery.
Web
Web touchpoints can move quickly from intent to action. Use web messaging for real-time updates, product changes, and experiences that reflect recent behavior.
Content Cards and other persistent in-product surfaces
Persistent in-app areas give customers a place to find information when it suits them, without a pop-up or interruption. They work well for “what’s new,” recommendations, education hubs, and loyalty progress.

Why channel combinations drive stronger retention and LTV
Cross-channel engagement builds momentum because each touchpoint can carry context forward. In the 2025 Braze Retail Customer Engagement Review, retailers who sent messages in one channel vs. none increased 90-day retention by 2.2x, and retailers who sent messages over two channels vs. one increased 90-day retention by 78%.
Braze research also found that using cross-channel messages vs. only in-product messages led to a 5x increase in customer lifetime value and a 6.4x increase in purchases per user.
Deloitte research also suggests strong omnichannel experiences translate into more expansion—customers reporting high-quality omnichannel experiences are 3.6x more likely to buy additional products and services.
Data, privacy, and trust in customer engagement strategy
First-party and zero-party data are the foundation of personalization today. Third-party data is harder to rely on, so engagement depends on what customers do across your channels, plus the preferences they share directly.
Trust comes down to how you collect and use that data. Brands must keep data collection purposeful, tie preference asks to clear value, and manage consent by channel and region.
A customer engagement platform supports privacy-forward engagement by activating these signals in real time, coordinating cross-channel journeys around behavior and preferences, and applying suppression and frequency controls so outreach stays consistent and respectful.
How AI and automation improve customer engagement strategy
AI and automation help teams respond faster to customer behavior. Automation runs the repeatable parts of lifecycle marketing. AI adds intelligence to decisions that change results, like who to prioritize, what to show, and how to keep journeys improving over time.
Predictive insights for segmentation and prioritization
Predictive AI helps teams focus effort where it matters. It uses first-party signals to identify customers more likely to convert, churn, repeat purchase, or upgrade, so journeys reflect risk and intent.
Use cases include improving early activation, flagging churn risk, and prioritizing high-intent customers for offers or education.
AI decisioning across channels
AI decisioning guides lifecycle personalization by helping to select the winning combinations of campaign variables for each customer, using the outcomes you choose to optimize for. That includes choices across message variants, featured products or services, promotions, channels, and delivery timing and frequency—all within the guardrails your team sets.
AI-assisted content creation, testing, and optimization
Generative AI can speed up content production and testing by creating message variants and personalized components. Combined with experimentation, it helps teams iterate on copy, offers, timing, and sequencing based on engagement and business outcomes.
Customer engagement strategy examples from leading brands
Seeing the same strategy applied in different ways is what makes customer engagement click. The five brands below show how teams translate first-party data into cross-channel journeys, then tie the work back to outcomes like retention, engagement, and revenue.
Wealthsimple turns a promotion into an acquisition and loyalty play
Wealthsimple is a Canadian money management platform built to help people manage, save, and grow their money through a suite of financial products.
The challenge
Wealthsimple wanted to deepen activation, monetization, and retention, but lacked the ability to run the personalized, automated campaigns needed to scale across the customer lifecycle.
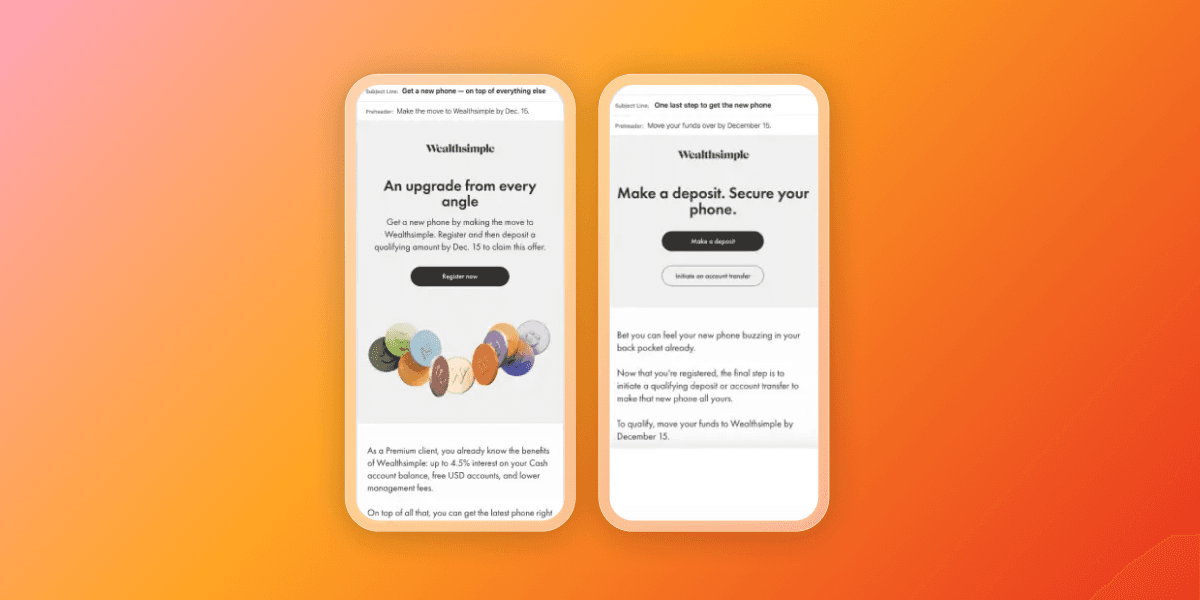
The engagement strategy
They used first-party data to orchestrate a promotional journey designed to encourage both new and existing customers to move assets to Wealthsimple and build a primary financial relationship.
Channels used
- In-app messages
- Content Cards
Business results
- 40% increase in quarterly net deposits, including a record month
- 20% of customers who received the campaign registered for the promotion
- 25% of participants were new customers
Quizlet’s progress emails keep learners coming back for more
Quizlet helps students and teachers study with digital learning tools, including flashcards, quizzes, and practice assessments.
The challenge
Quizlet needed a more efficient way to pull user activity data and turn it into personalized updates for students and teachers.
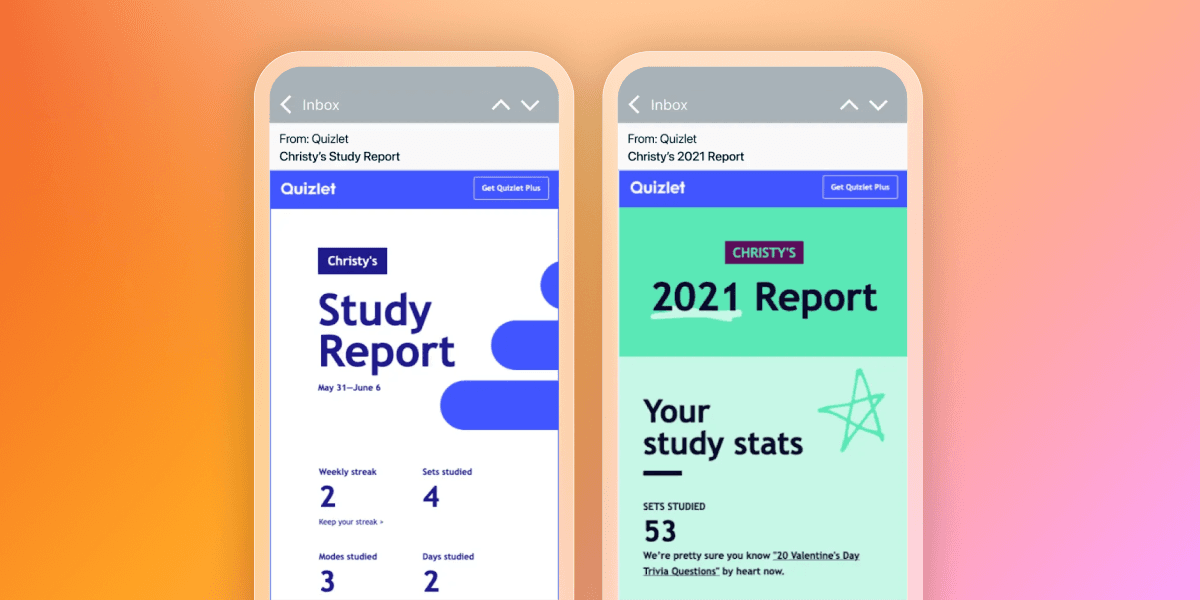
The engagement strategy
They used Connected Content to dynamically populate weekly recap emails with individual study habits and app usage, giving learners a clear view of progress and momentum.
Channels used
Business results
- Nearly 17 million incremental learning sessions
- Over two million incremental monthly active users (MAU)
- More than 2,500 incremental subscribers
Canva scales email volume, keeps deliverability, and lifts engagement
Canva is a global design platform that helps people create professional-looking content quickly, across a wide range of use cases.
The challenge
Canva needed to reach millions of users with content that felt relevant and helpful, across many markets and languages, while maintaining deliverability during a period of rapid change.
The engagement strategy
Canva used Braze to scale weekly email volumes and speed up localization, keeping content aligned to user interests across regions.
Channels used
Business results
- Weekly email volume grew from 30 million to 50 million
- 99% email deliverability while scaling volume
- 33% increase in open rates
- 2.5% increase in platform engagement
Wellhub (formerly Gympass) personalizes wellness journeys at scale
Wellhub runs a global network of gyms, studios, trainers, and wellbeing apps, working with employers to offer wellness benefits to employees.
The challenge
Wellhub needed a way to run meaningful, hyper-personalized engagement at scale, with journeys that reflected individual goals across a B2B2C model.
The engagement strategy
Deliveroo used Currents to stream Braze data into their analytics stack (including Looker), giving teams real-time visibility into campaign performance and the ability to explore insights by region.
Channels used
- Mobile push notifications
- Currents (data streaming to BI and warehousing)
Business results
- 8X reduction in time spent fielding data requests
How to measure customer engagement strategy success
A customer engagement strategy is working when customers come back more often, stay longer, and generate more value over time. Track a small set of metrics consistently, and look at them by lifecycle stage and cohort, not just in aggregate.
Retention and churn
Retention shows whether customers keep coming back. Churn shows where the relationship breaks. Track both overall and early lifecycle windows (like days 7, 14, and 30), and watch for drop-off around activation milestones.
Customer lifetime value (LTV)
LTV shows whether engagement is driving long-term value. Use it to compare journey performance, incentives, and loyalty programs, and to measure lift for customers who saw a journey vs. a holdout group.
MAU/WAU and engagement frequency
Monthly active users (MAU) and weekly active users (WAU) show whether customers are active. Engagement frequency shows how active they are. Pair them with repeat behaviors that signal value, like sessions, purchases, or key feature usage.
Revenue per user
Revenue per user connects engagement to outcomes without waiting for a full LTV window. Track it by segment and journey exposure to see which journeys are moving revenue, and where you’re over-discounting.
Cross-channel engagement and conversion rates
Cross-channel performance shows whether orchestration is working. Look at journey-level conversion, channel assist patterns (like an in-app message followed by an email conversion), and fatigue signals like opt-outs, unsubscribes, and suppressed sends.
Common customer engagement strategy mistakes (and how to avoid them)
Even strong teams run into challenges once engagement spans more channels, more journeys, and more stakeholders. Here are four common mistakes, plus straightforward ways to fix them.
Over-prioritizing acquisition over retention
When retention doesn’t have clear goals, teams drift back toward top-of-funnel volume.
What to do instead:
- Set lifecycle goals alongside acquisition goals (activation, repeat purchase, retained MAU)
- Invest early in onboarding and first-value milestones
- Use loyalty and proactive engagement to reduce reliance on constant discounting
Operating channels and teams in silos
Silos create duplicated messaging, conflicting offers, and inconsistent CX. They also slow improvement because performance gets measured channel by channel.
What to do instead:
- Align on shared segments, priority journeys, and channel roles
- Coordinate sequencing, prioritization, and suppression across channels
- Standardize key events and reporting so teams work from the same inputs
Letting journeys go stale due to limited experimentation
Customer behavior changes. Products change. Journeys that don’t get revisited lose impact.
What to do instead:
- Keep a simple testing backlog for each core journey (targeting, timing, creative, and offers)
- Revisit frequency and suppression as channel mix expands
- Use holdouts on foundational journeys to measure lift
- Choose AI decisioning for constant experimentation and optimization
Implementing tools without a clear engagement strategy
Tools help you execute. Strategy defines what you’re building and why. Without the strategy, it’s difficult to identify what’s actually working.
What to do instead:
- Define outcomes, audiences, and lifecycle moments before you build
- Start with a small set of core journeys, then expand
- Use AI where it improves personalization, prioritization, and optimization, based on first-party data
Customer engagement strategy FAQs
Is customer retention more important than customer acquisition?
Customer retention is often more important than customer acquisition because it increases customer lifetime value and reduces reliance on paid growth. Retention improves faster when your customer engagement strategy focuses on activation, loyalty, and early risk signals.
Is customer engagement time-consuming?
Customer engagement does not have to be so time-consuming if you use automation to handle repeatable tasks across the lifecycle. It becomes easier to manage when you set shared triggers, rules, and cross-channel coordination.
Is customer engagement only about mobile marketing?
Customer engagement is not only about mobile marketing because customers move between email, web, SMS, push notifications, and in-app experiences. A digital customer engagement strategy keeps context consistent across devices and touchpoints.
What is CRM customer engagement?
CRM customer engagement is typically the sales and service activity tracked in a CRM, like outreach, follow-ups, and support history. It focuses on records and workflows, while a customer engagement strategy uses first-party behavior to orchestrate lifecycle journeys across channels.
How can a customer engagement strategy benefit businesses?
A customer engagement strategy can benefit businesses because it improves retention, conversion, revenue per user, and loyalty through more relevant lifecycle experiences. It also helps reduce message fatigue and track progress using engagement metrics.
What tools are needed to implement a customer engagement strategy?
The tools needed to implement a customer engagement strategy typically include first-party data collection, preference and consent management, analytics, and a platform for customer journey orchestration across channels. Many teams also use AI to support prioritization, personalization, and optimization.
How can Braze help companies implement their customer engagement strategy?
Braze can help companies implement their customer engagement strategy by supporting cross-channel journey orchestration, personalization, and measurement powered by first-party data. Braze also supports AI-powered engagement across predictive capabilities, generative workflows, and AI decisioning.
Why is increasing customer engagement important?
Increasing customer engagement is important because it improves retention and customer lifetime value and reduces churn risk. It also creates more first-party signals you can use to keep personalization accurate over time.
What is a customer engagement strategy vs. general marketing strategy?
A customer engagement strategy is different from a general marketing strategy because it focuses on lifecycle relationships and ongoing interactions across channels. A general marketing strategy typically covers positioning, audience strategy, and campaign planning, including brand and customer acquisition work.
What are the most important customer engagement channels and touchpoints?
The most important customer engagement channels and touchpoints depend on your customers, as behavior varies by category and product. Common touchpoints include email, push notifications, SMS, in-app messages, web, and persistent in-product surfaces like Content Cards.
How can AI and automation improve customer engagement strategy?
AI and automation can improve customer engagement strategy because they help teams prioritize audiences, personalize messaging, and optimize campaign variables over time. They also speed up testing and iteration across content, timing, and channel choices.
How do you measure the success of a customer engagement strategy?
How do you measure the success of a customer engagement strategy?
You measure the success of a customer engagement strategy by tracking retention and churn, customer lifetime value, engagement frequency, revenue per user, and journey-level conversion across channels. Controlled tests and holdouts help show which changes drove lift.
What are examples of customer engagement strategies from leading brands?
Examples of customer engagement strategies from leading brands include onboarding and activation journeys, education and feature discovery, loyalty and growth programs, and churn prevention and win-back flows. These strategies typically run across email, push, SMS, in-app, and web touchpoints.
Related Tags
Be Absolutely Engaging.™
Sign up for regular updates from Braze.
Related Content
 Article12 min read
Article12 min readLeaders in marketing: Celebrating the women redefining customer engagement on International Women’s Day
March 09, 2026 Article4 min read
Article4 min readClosing the retail experience divide
March 09, 2026 Article5 min read
Article5 min readRamadan revelations: Mastering customer engagement in MENAT with AI
March 06, 2026